Objective
Analysis of gene expression with quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) will be a component of the in vivo nickel exposure work conducted in autumn 2023. Four experiments were completed using a high and low dose of nickel chloride (5 and 45 mg L-) and we are aiming to evaluate the impact of nickel toxicity on gene expression relating to oxidative stress, senescence, stemness, and apoptosis.
Background
Refer to pilot exposure post for more details regarding procedures and experimental design.
Experiment was repeated three more times after pilot exposure to increase the number of replicates per treatment.
Final experimental set up
| Nickel Concentration (mg/L) | Exposure Length (hrs) | Number of Replicates |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24 | 14 |
| 5 | 24 | 13 |
| 45 | 24 | 12 |
Protocol leading to cDNA synthesis
RNA extracted using Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit with 10% β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) in RLT buffer and QiaShredder column step supplemented to protocol.
Quantify RNA with NanoDrop.
gDNA elimination with routine DNAse treatment with Invitrogen TURBO DNA-free Kit (Cat. No. AM1907).
| gDNA Elimination Component | per 1 rxn (uL) |
|---|---|
| 10x DNase Buffer | 2 |
| Turbo Enzyme | 1 |
| RNA sample | 20 |
| Total | 23 |
2uL of DNase Inactivation Reagent used towards end of protocol.
- Requantification of gDNA eliminated RNA with Nano Drop:
| Date | Sample ID | RNA Concentration (ng/uL) | A260/A280 | 260(10mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 0-R1 pilot | 19.2 | 1.55 | 0.48 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 0-R2 pilot | 113.2 | 1.85 | 2.83 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 0-R3 pilot | 152.4 | 1.87 | 3.809 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 0-R4 pilot | 67.1 | 1.77 | 1.676 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 5-R1 pilot | 22.4 | 1.66 | 0.56 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 5-R2 pilot | 30.6 | 1.68 | 0.764 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 5-R3 pilot | 29 | 1.67 | 0.726 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 5-R4 pilot | 45.1 | 1.77 | 0.128 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 45-R2 pilot | 87.6 | 1.82 | 2.14 |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 45-R3 pilot | 13.8 | 1.47 | |
| 09/30/2023 | 9302023 45-R4 pilot | 84.8 | 1.83 | 2.12 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 0-R1 E1 | 12.1 | 1.55 | 0.305 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 0-R2 E1 | 45.9 | 1.83 | 1.148 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 0-R3 E1 | 78.4 | 1.85 | 1.959 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 0-R4 E1 | 38.5 | 1.8 | 0.962 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 5-R1 E1 | 83.3 | 1.82 | 2.082 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 5-R3 E1 | 27.1 | 1.69 | 0.676 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 5-R4 E1 | 69.5 | 1.84 | 1.737 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 45-R1 E1 | 50 | 1.78 | 1.249 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 45-R2 E1 | 57.3 | 1.84 | 1.433 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 45-R3 E1 | 43.5 | 1.73 | 1.087 |
| 10/25/2023 | 10252023 45-R4 E1 | 60.1 | 1.83 | 1.505 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 0-R1 E2 | 86.5 | 1.86 | 2.163 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 0-R2 E2 | 54.7 | 1.66 | 1.367 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 0-R3 E2 | 37.4 | 1.72 | 0.935 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 5-R1 E2 | 58.4 | 1.66 | 1.459 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 5-R2 E2 | 69.7 | 1.69 | 1.743 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 5-R3 E2 | 33.7 | 1.51 | 0.843 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 45-R2 E2 | 34.5 | 1.44 | 0.863 |
| 11/15/2023 | 11152023 45-R3 E2 | 16.2 | 1.5 | 0.405 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 0-R1 E3 | 72.4 | 1.78 | 1.809 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 0-R2 E3 | 60.3 | 1.78 | 1.507 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 0-R3 E3 | 21.4 | 1.61 | 0.534 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 5-R1 E3 | 12.7 | 1.43 | 0.318 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 5-R2 E3 | 15.5 | 1.57 | 0.387 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 5-R3 E3 | 64.4 | 1.76 | 1.609 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 45-R1 E3 | 80.6 | 1.82 | 2.016 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 45-R2 E3 | 49.3 | 1.77 | 1.231 |
| 11/29/2023 | 11292023 45-R3 E3 | 64.3 | 1.79 | 1.607 |
RNA quality drop difference of about 0.2 after gDNA elimination.
- cDNA synthesis with SuperScript IV VILO Kit.
| cDNA synthesis Component | per 1 rxn (uL) |
|---|---|
| SuperScript IV VILO Master Mix | 2 |
| Nuclease-free water | variable |
| RNA sample | variable |
| Total | 10 |
Final mass of 96.8 ng of RNA in reaction mix for each sample (thus variable water and RNA volumes)
cDNA Pool
It is not recommended to NanoDrop cDNA as readings below may be inaccurate due to residual nucleotide and etc. from the synthesis reaction. Assume the reaction is a 1:1 RNA:cDNA.
cDNA pool spectrometer readings and dilutions:
| Date Made | Sample | cDNA ng/uL | A260/A280 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12/18/2023 | Original Pool | 2231.2 | 1.73 |
| 1/14/2024 | 10-2 | 223.12 | 1.73 |
| 1/14/2024 | 10-3 | 22.312 | 1.73 |
| 1/14/2024 | 10-4 | 2.312 | 1.73 |
| 1/14/2024 | 10-5 | 0.2312 | 1.73 |
| 1/14/2024 | 10-6 | 0.02312 | 1.73 |
Primers
Primers for Botryllus schlosseri designed as described in Tunicate Primers notebook entry.
| Number | Gene | Forward Primer (5’-3’) | Reverse Primer (5’-3’) | NCBI Accession Number (If complete CDS) | Botryllus Contig Sequence (if no complete CDS was found) | Amplicon Length | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BAX | CATTGACCTTGCGTGTTATTGG | AAGATGTCCTTGGTGGGTTG | KU948200.1 | None | 97 | in house |
| 2 | POU3 | CAGTAGGTCTTCGCATCCATC | CGTTTGCATCGTTGGTGTAAG | KU948203.1 | None | 80 | in house |
| 3 | PolB | GGCTTCACAATCAATGAGTATTCC | AGCAATCTTTCCGCATTCATTC | None | botctg092056 | NA | in house |
| 4 | TNF | GTTTCAGTCAACACCTTGTGTC | AATCTCGACCGCTGACTTATAC | None | botctg065850 | 131 | in house |
| 5 | SOXB1 | GGGAATGTGTTCATCCTCTGG | TGAATCCAGGAGTTACTCAAGTTC | KU948203.1 | None | 116 | in house |
| 6 | MYC | GAAGTCCTGGCTAAGATGCTAC | AGCGTCAAGAAGGAAGTACG | KU948203.1 | None | 119 | in house |
| 7 | AIF1 | GGATTCTCTCACCGATGGAATAG | CCTGACTTGGAGCCTTTATGG | KU948202.1 | None | 102 | in house |
| 8 | SOD1 | CAATCCATATAACAAGGTTCATGGC | TGATATCCACACAGGCACAAC | EE743567.1 | None | 107 | in house |
| 9 | PARP1 | AATTTGGCACCGCTCATTTC | TGCAAGACCTTCAGCTTCTC | KU948201.1 | None | 94 | in house |
| 10 | SIRT6 | ATTAGTACCGCGTCTGGAATAC | GGATGGAATCGCTTCTTCAAATC | None | botctg109566 | 114 | in house |
| 11 | IAP7 | GGTCTCTTCACGGACATCTTC | GCTCAGTATGTTGTGCTTGTTC | KU948203.1 | None | 111 | in house |
| 12 | HSP70 | CGAGAAGTTGAAGGACAAGATCTCCG | TCTCTGCAGTCTGGTTGTTGTCGAGC | NA | NA | NA | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.023 |
| 13 | Mortalin | TTCATGATACCGAAACCAAGATGGACG | AATTTCCTCCTTGATGGCATCCACC | KY212120.1 | None | 79 | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.023 |
| 14 | ACTb | GTAGGTAGTCTCGTGAATTC | CACGCCATCTTGCGTCTGGA | NA | NA | 321 | doi:10.1016/j.dci.2006.12.009 |
| 15 | 18s | GGCAGCCTCCGGGAAACCAAAGTC | CTGGTGGTGCCCTTCCGTCAATTC | NA | NA | NA | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.023 |
End-Point PCR

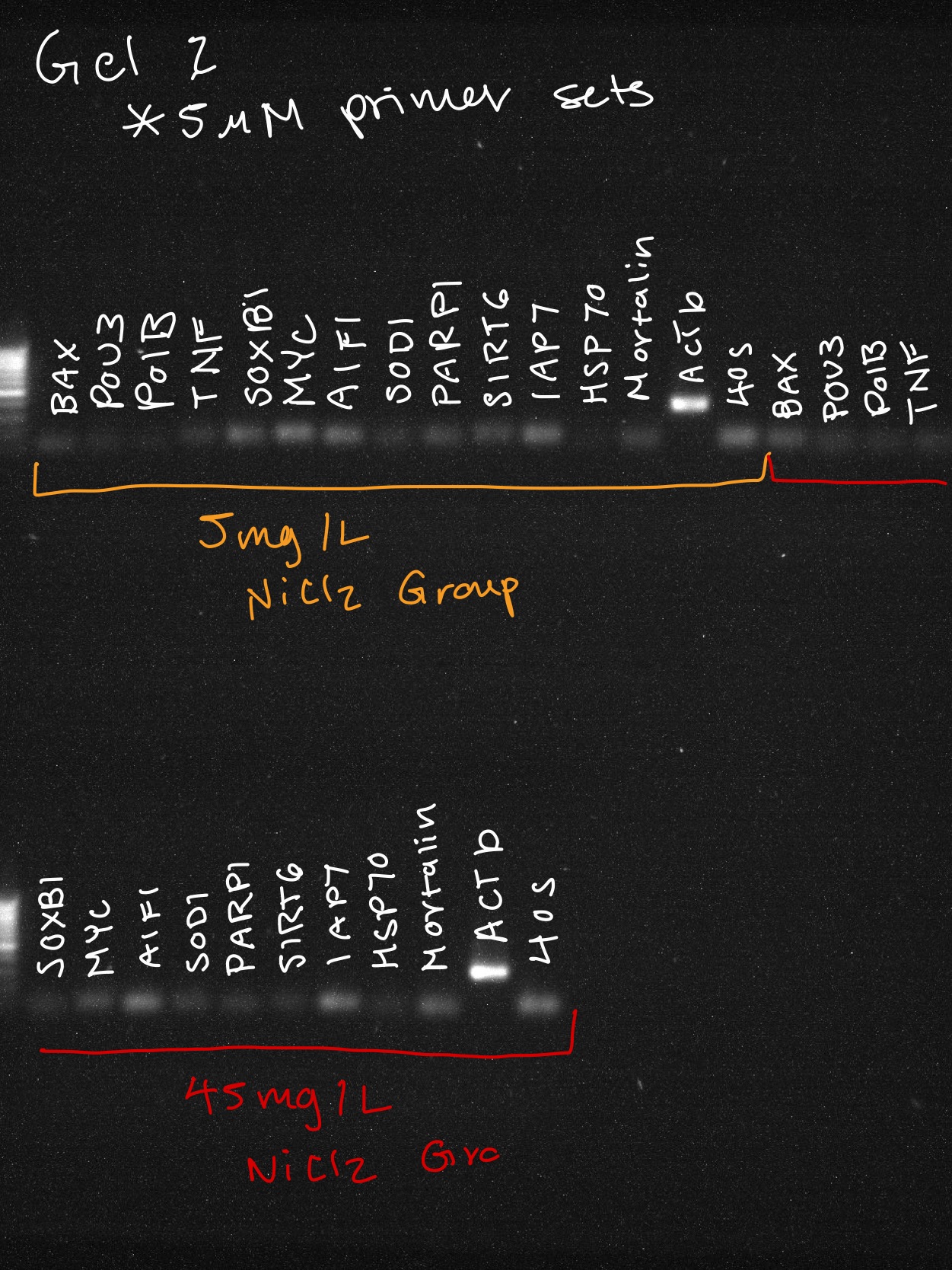
EP-PCR Reaction Info
| EP-PCR Component | per 1 rxn (uL) |
|---|---|
| PCR Master Mix (ThermoFisher) | 12.5 |
| Nuclease-free water | 9.5 |
| Forward Primer (5 uM) | 1 |
| Reverse Primer (5 uM) | 1 |
| 1:3 dilution of pooled (per treatement) cDNA | 1 |
| Total | 25 |
Final concentration of 200 nM of each primer per 1 rxn.
Gel Info
With 1x TAE buffer on 1% agarose gel:
| Component | per 1 rxn (uL) |
|---|---|
| Nuclease-free water | 5 |
| cDNA (after EP-PCR) | 5 |
| Loading Dye | 2 |
| Total | 12 |
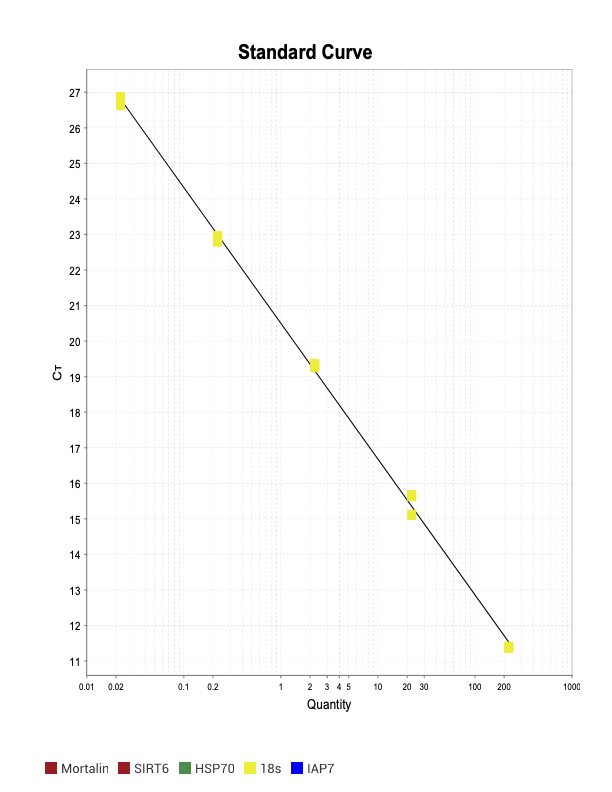
Relative Standard Curves
To view data and results directly from plate reader view:
qPCR Reaction Information
| Component | per 1 rxn (uL) |
|---|---|
| Applied Biosystems™ PowerSYBR™ Green PCR Master Mix | 5 |
| Nuclease-free water | 3.5 |
| Forward Primer (2.5 uM) | 0.25 |
| Reverse Primer (2.5 uM) | 0.25 |
| cDNA | 1 |
| Total | 10 |
Final concentration of 62.5 nM of each primer per 1 rxn (suggested to be within 50-300 nM for this protocol).
Cycle Information
| Stage | Step | Temperature (C) | Duration (sec) | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hold | Hold | 50 | 120 | 1 |
| Hold | Hold | 95 | 600 | 1 |
| PCR | Denature | 95 | 15 | 40 |
| PCR | Anneal/Extend | 60 | 60 | 40 |
| Melt Curve | Denature | 95 | 15 | 1 |
| Melt Curve | Anneal/Extend | 60 | 60 | 1 |
| Melt Curve | Dissociation | 95 | 1 | 1 |
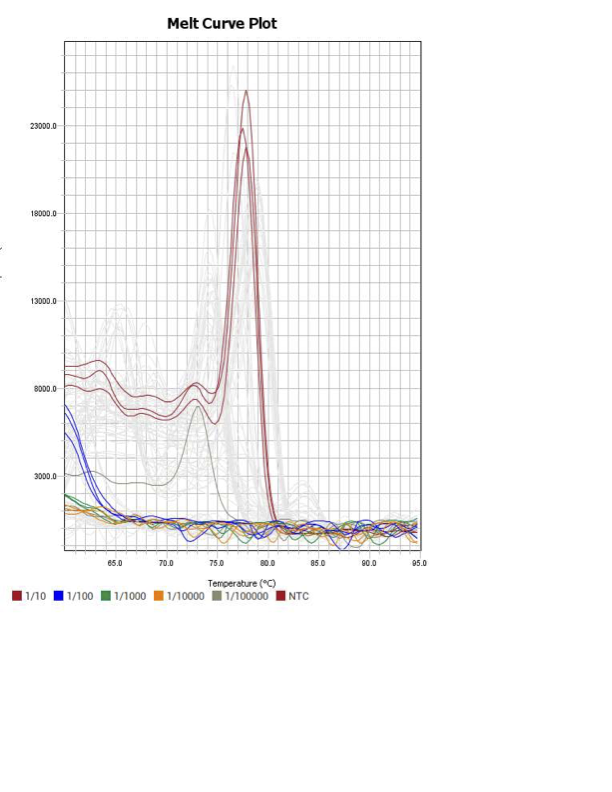
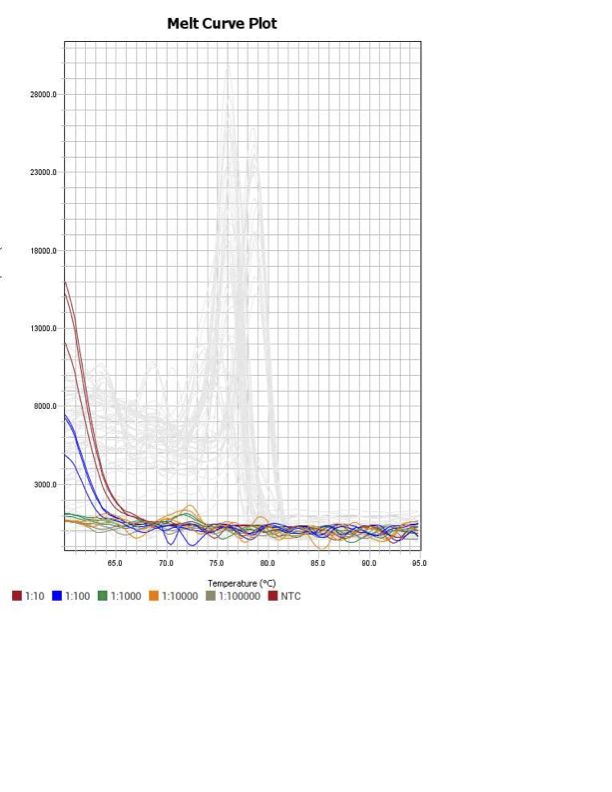
NTC results
| Target Name | Task | CT |
|---|---|---|
| BActin | NTC | Undetermined |
| BAX | NTC | 32.548 |
| SOD1 | NTC | 26.921 |
| SIRT6 | NTC | Undetermined |
| IAP7 | NTC | 32.048 |
| HSP70 | NTC | Undetermined |
| Mortalin | NTC | 32.660 |
| 18s | NTC | 32.623 |
| POU3 | NTC | 33.793 |
| PolB | NTC | Undetermined |
| TNF | NTC | Undetermined |
| MYC | NTC | 32.153 |
| AIF1 | NTC | 27.873 |
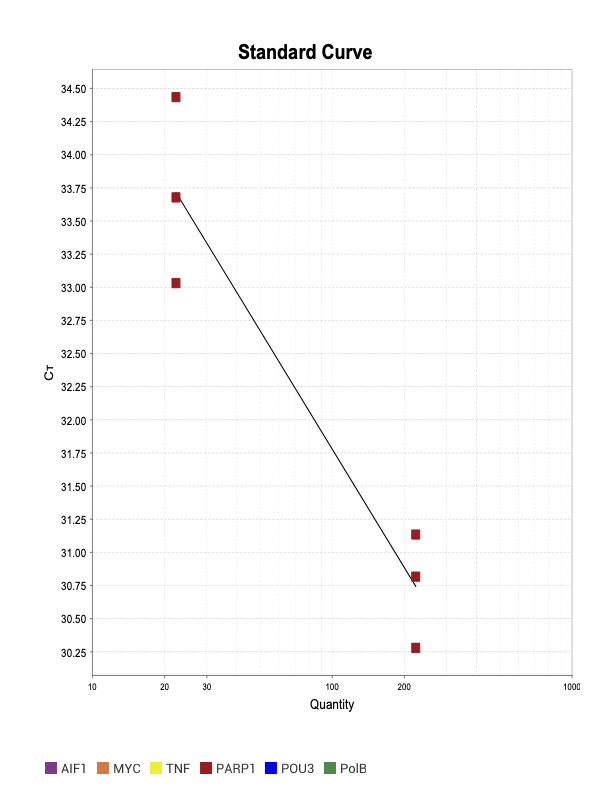
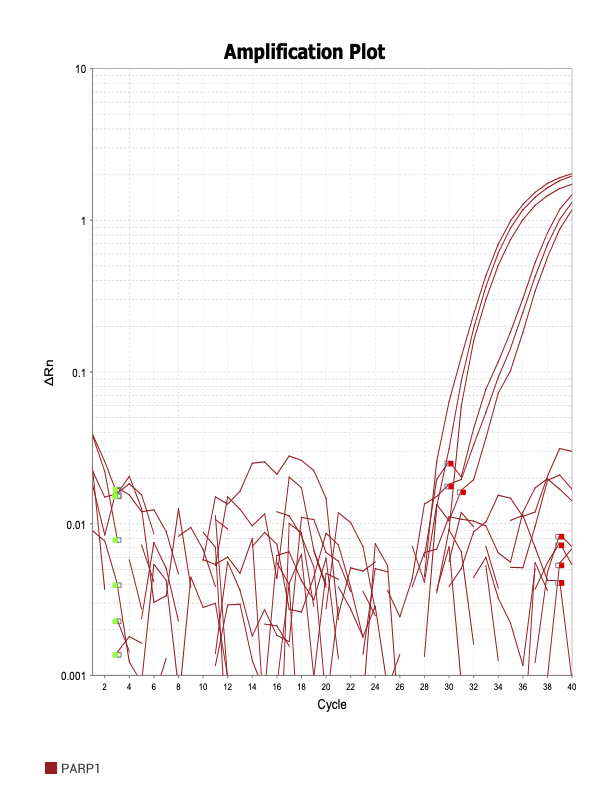
| PARP1 | NTC | Undetermined |
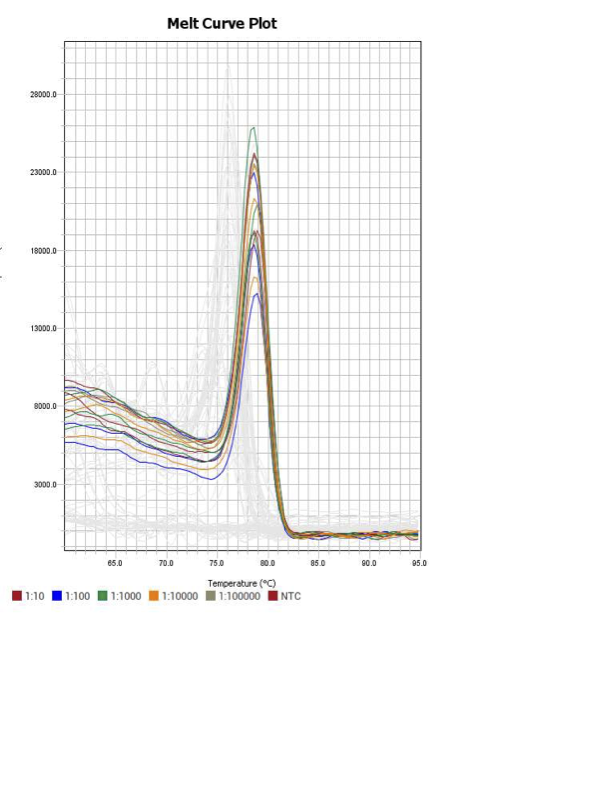
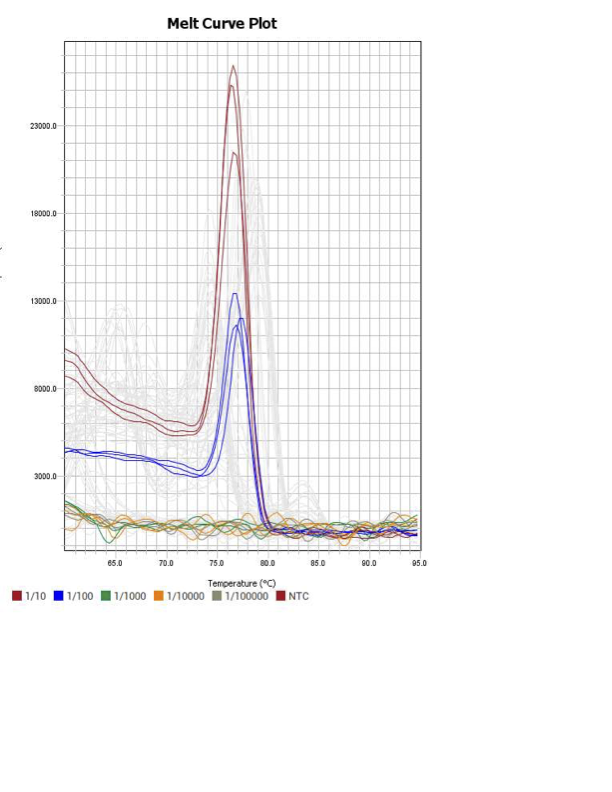
Good
Beta actin
The two primer sets with acceptable efficiency values in my qPCR are my housekeeping (HK) genes. I suspect given they are constitutively and highly expressed, issues with inhibitors in the reaction mix are not as much of an issue relative to my genes of interest (GOI).
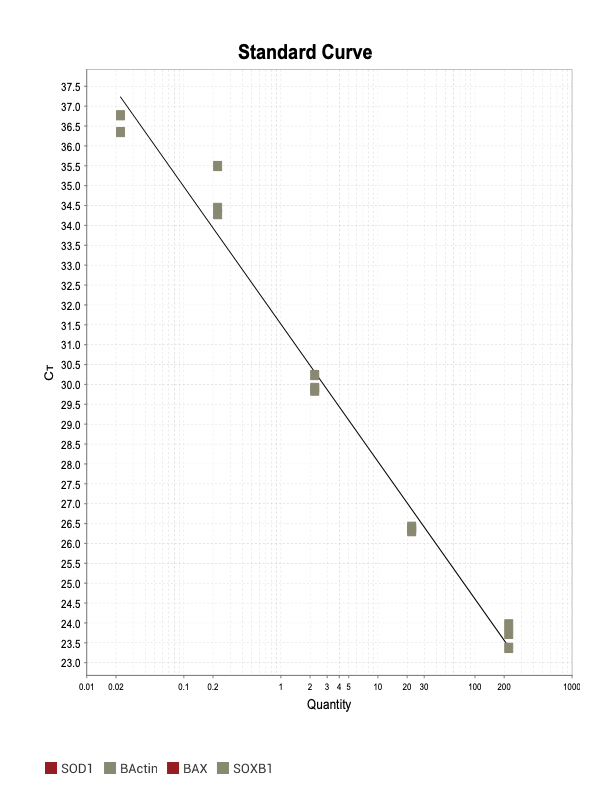
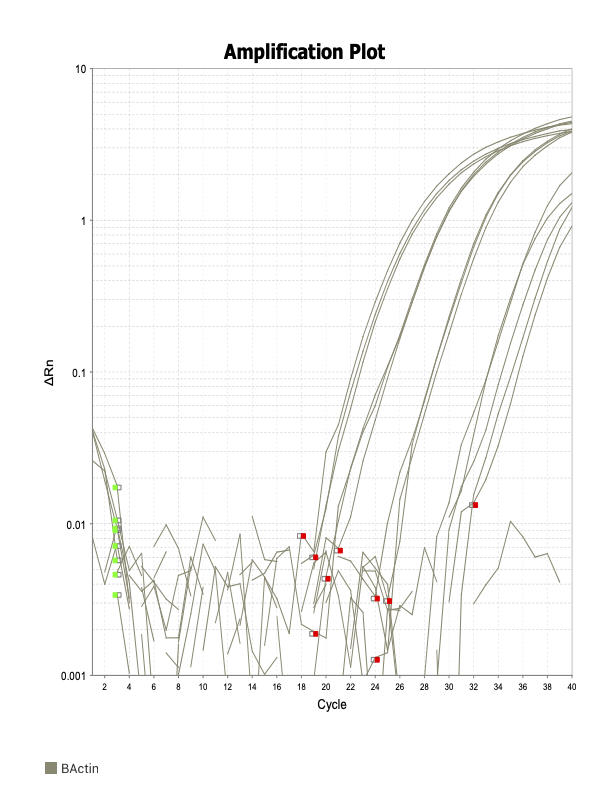
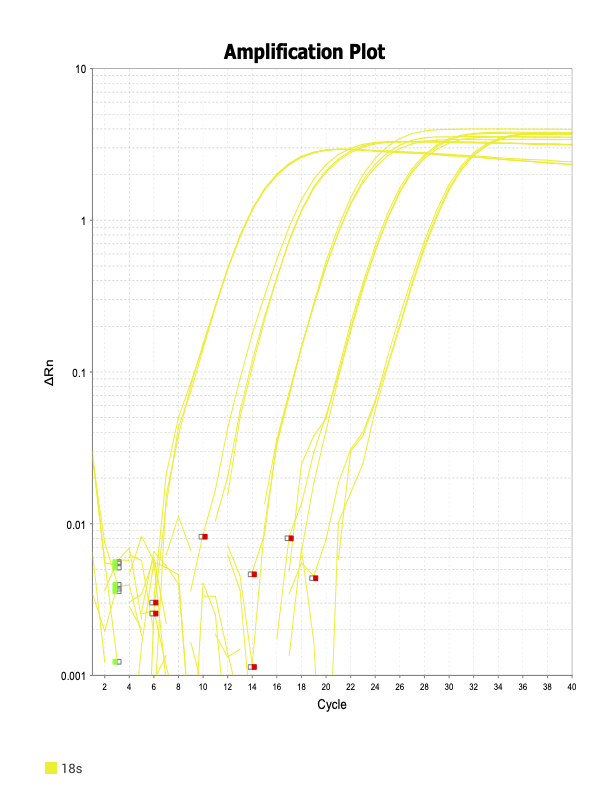
18s
Questionable
BAX
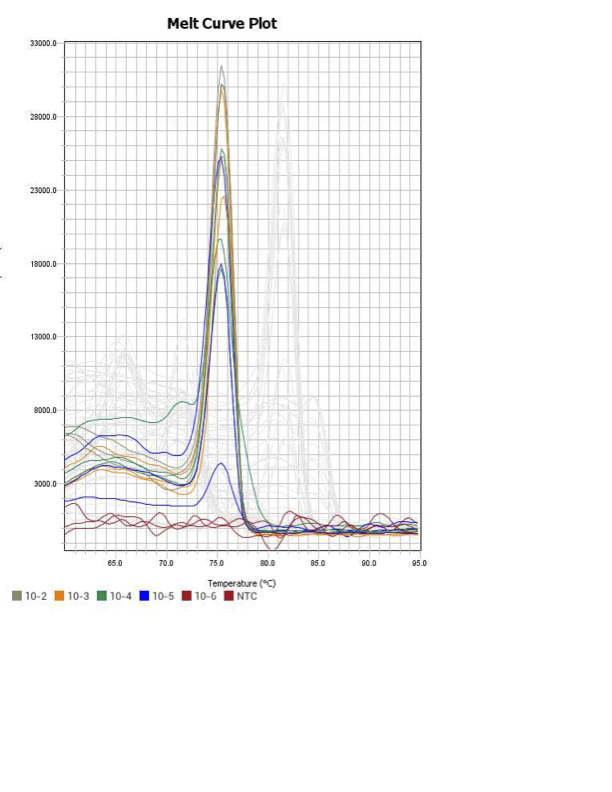
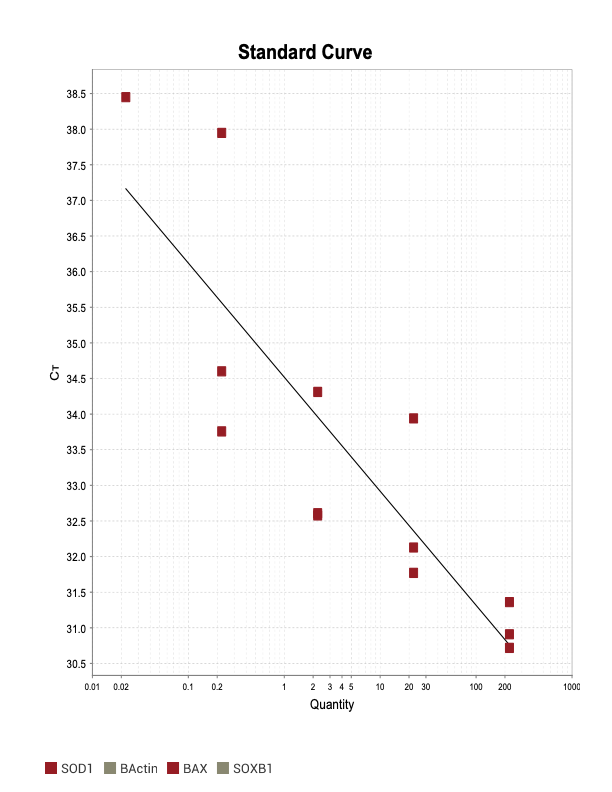
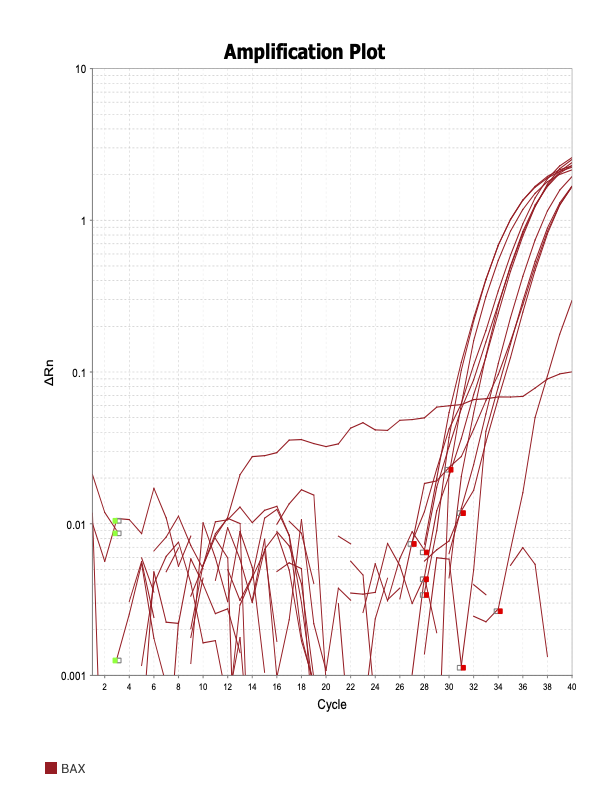
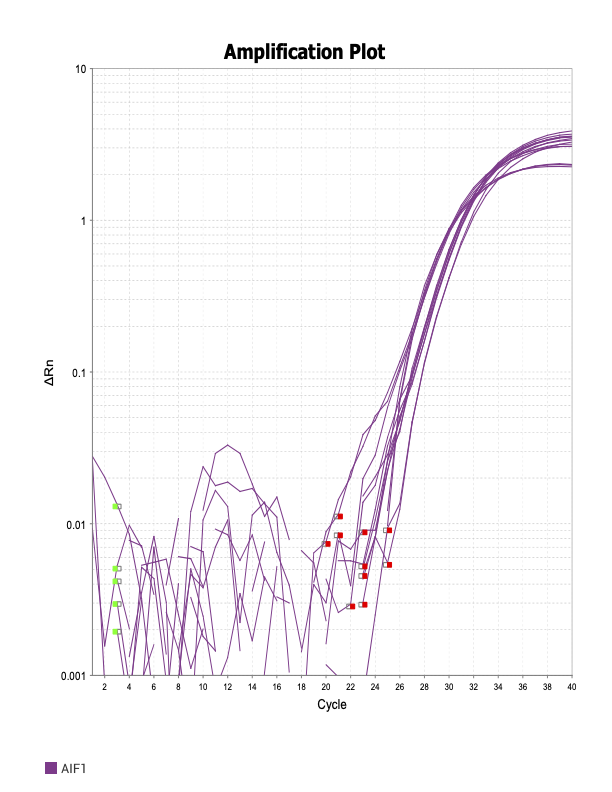
AIF1
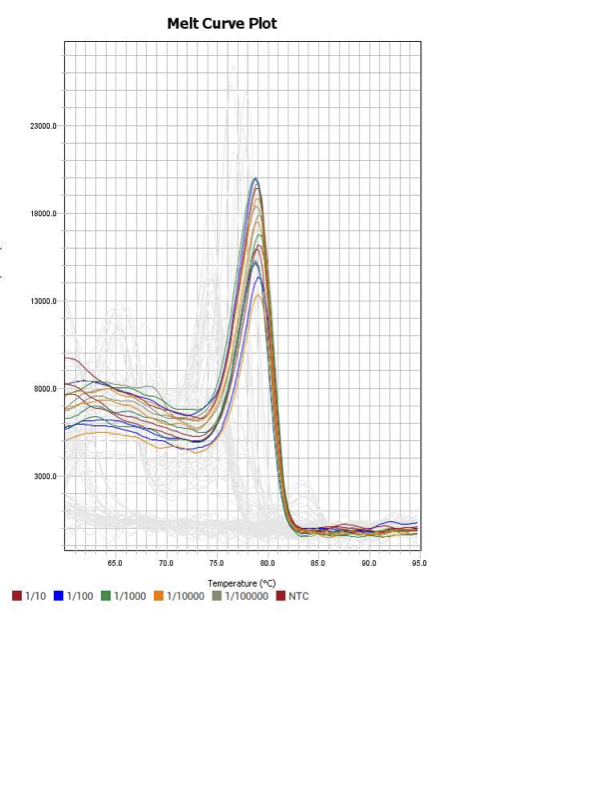
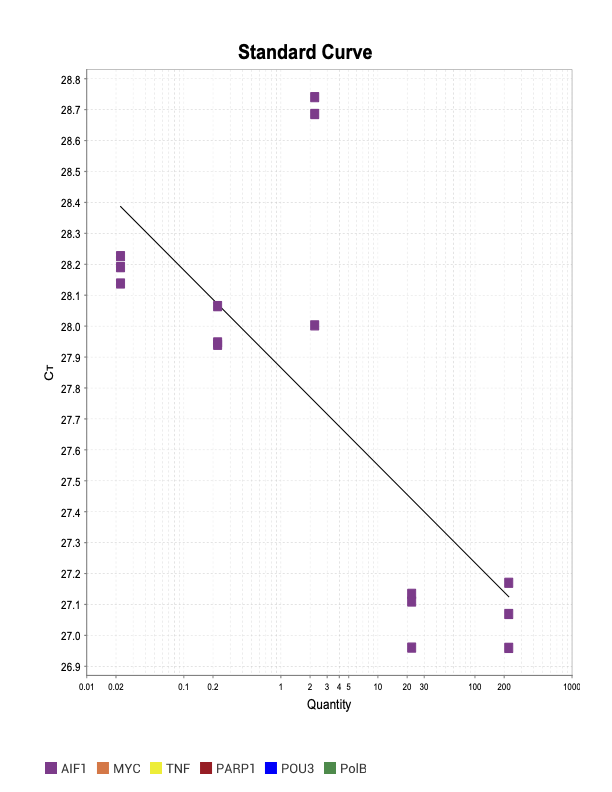
Mortalin
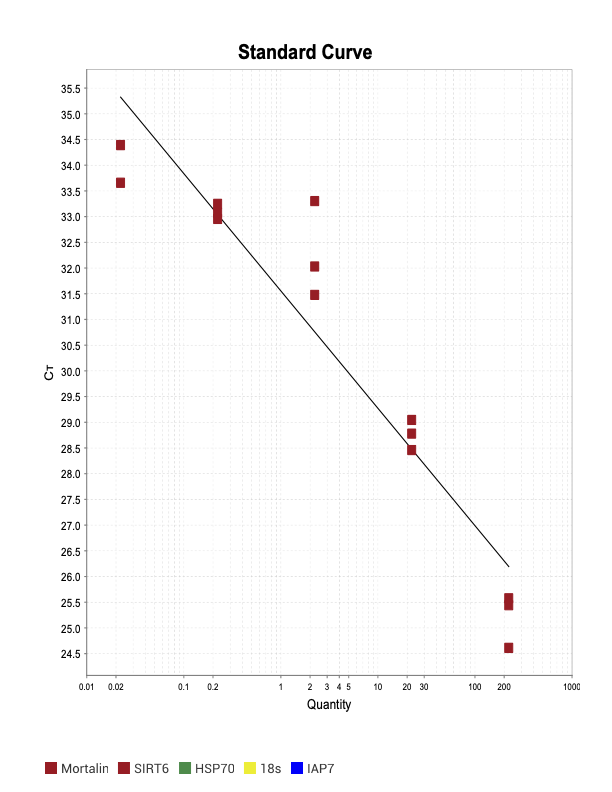
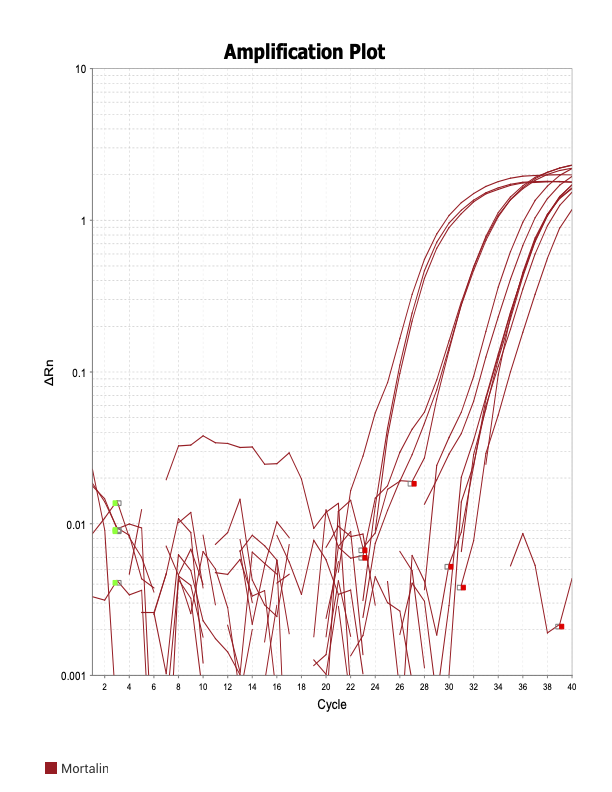
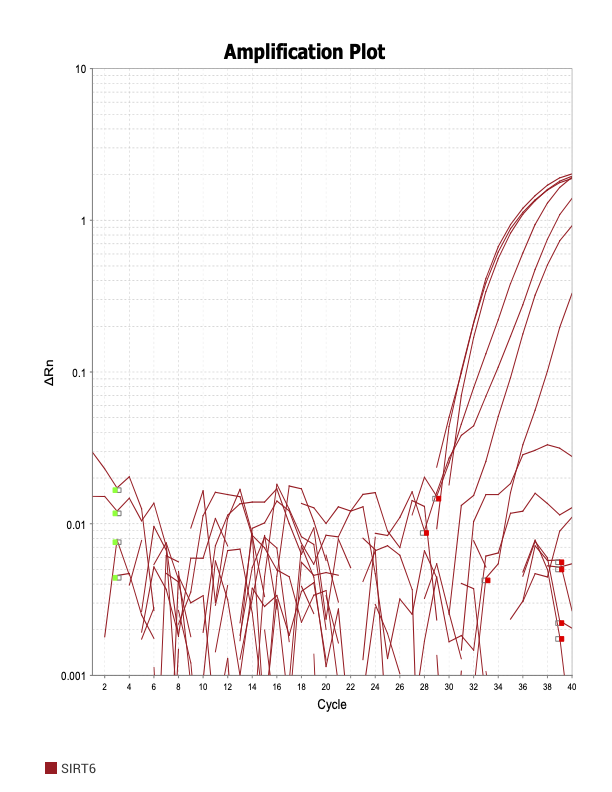
SIRT6
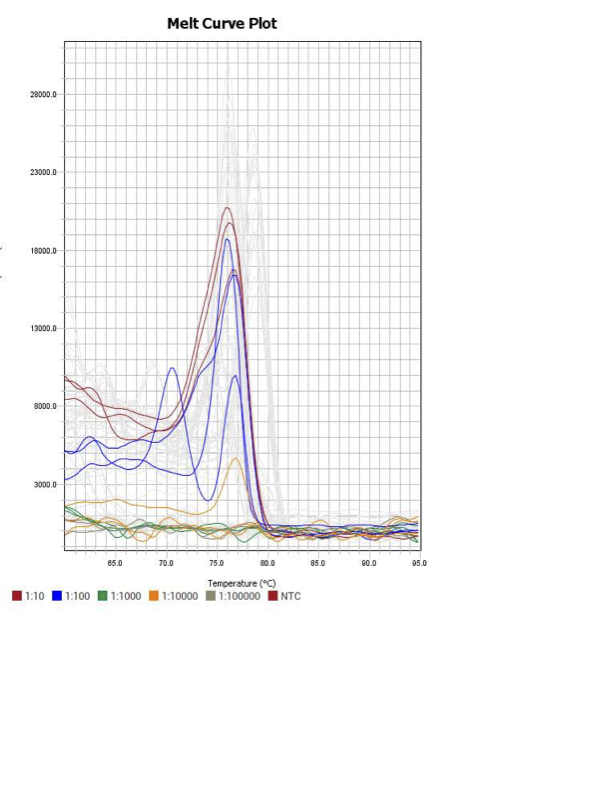
SOD1
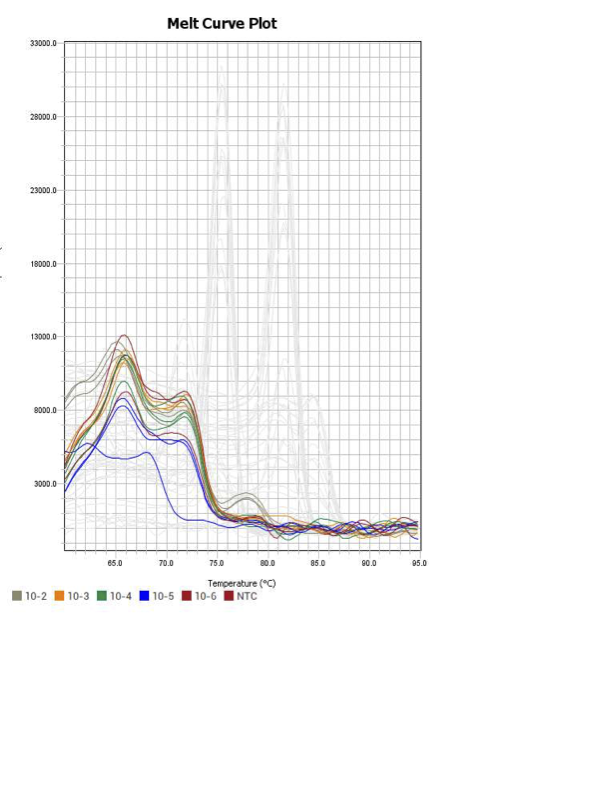
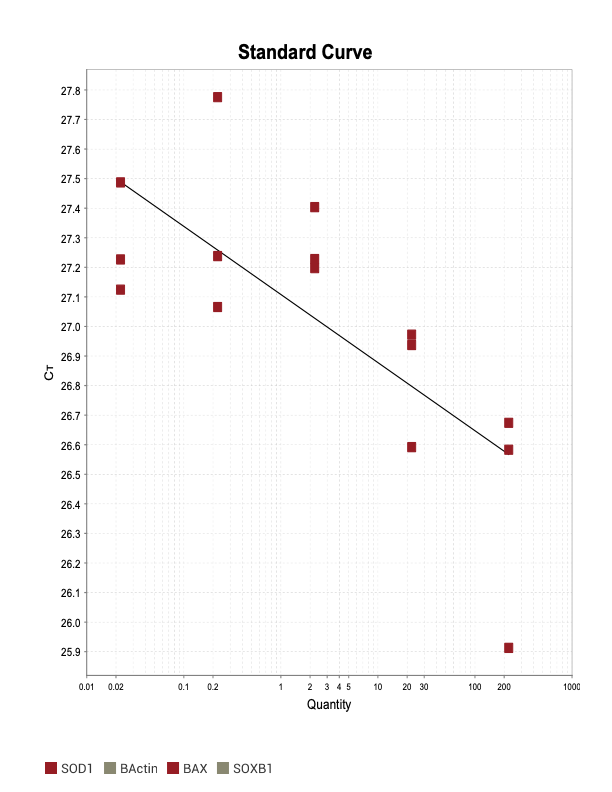
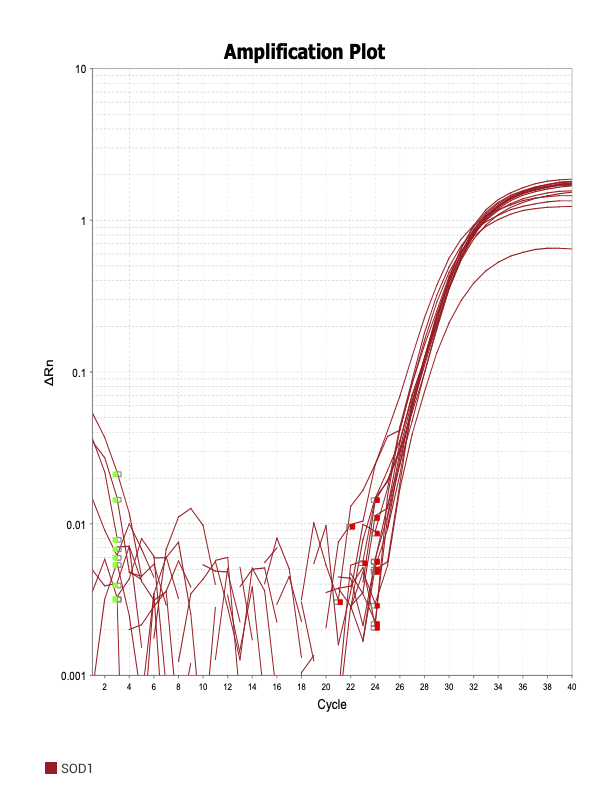
POU3
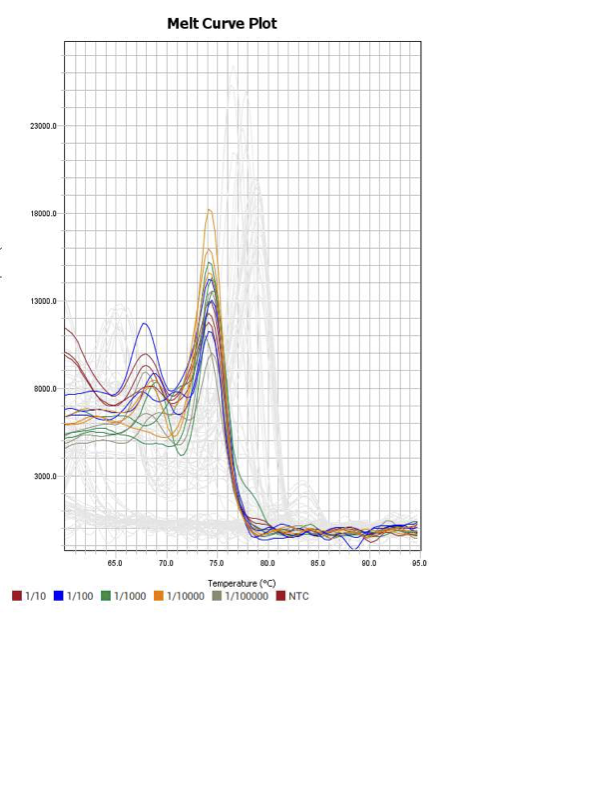
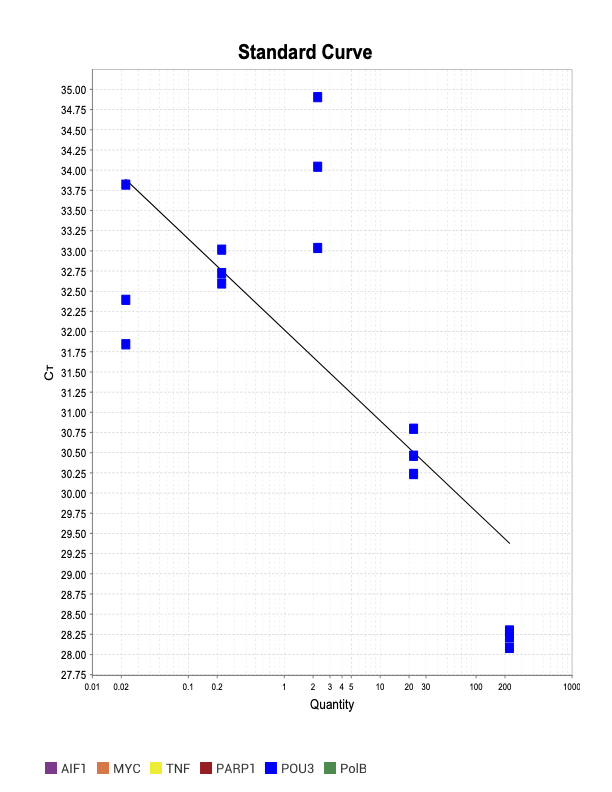
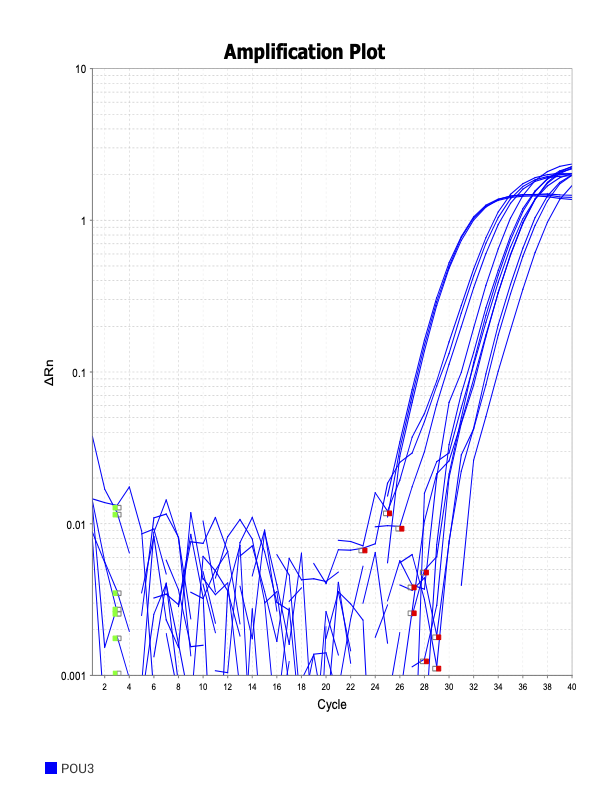
SOXB1
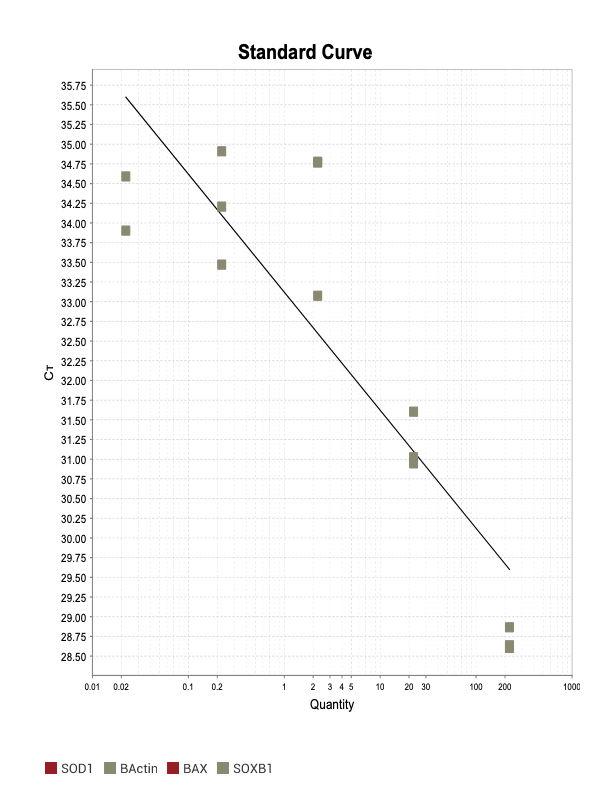

MYC
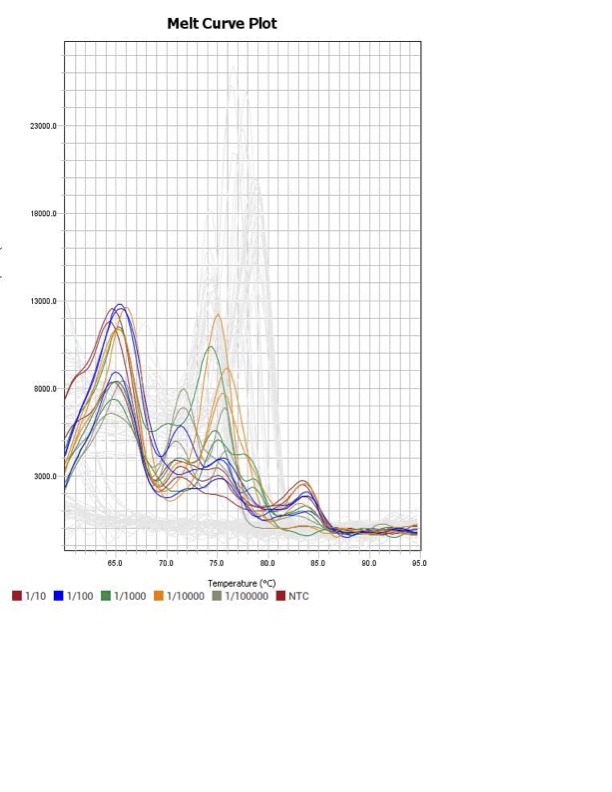
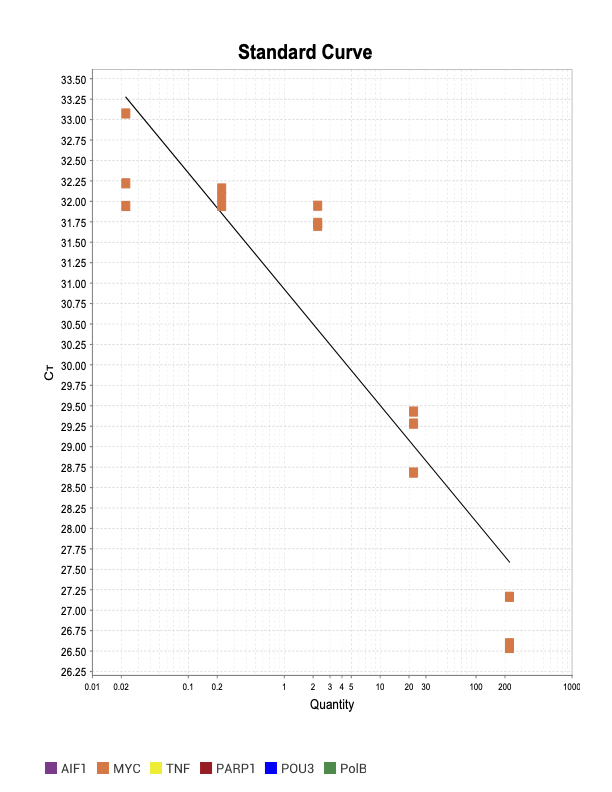
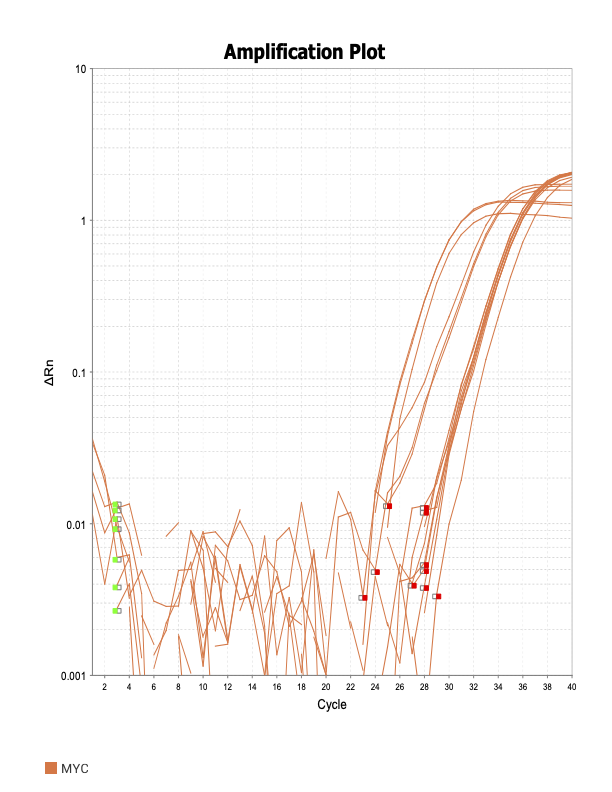
IAP7
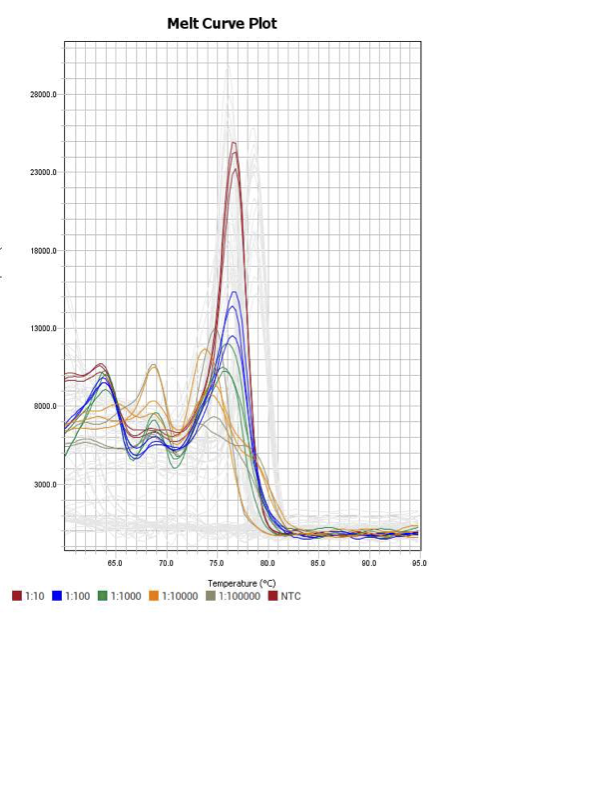
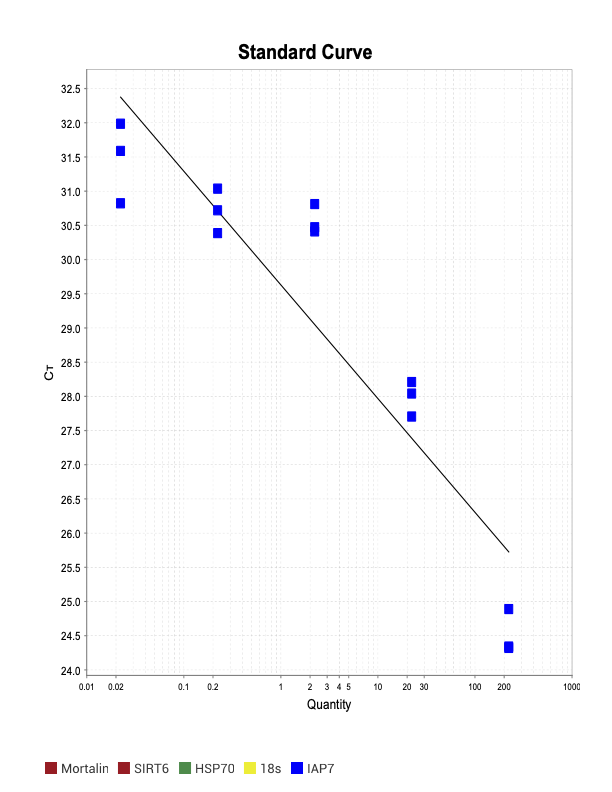
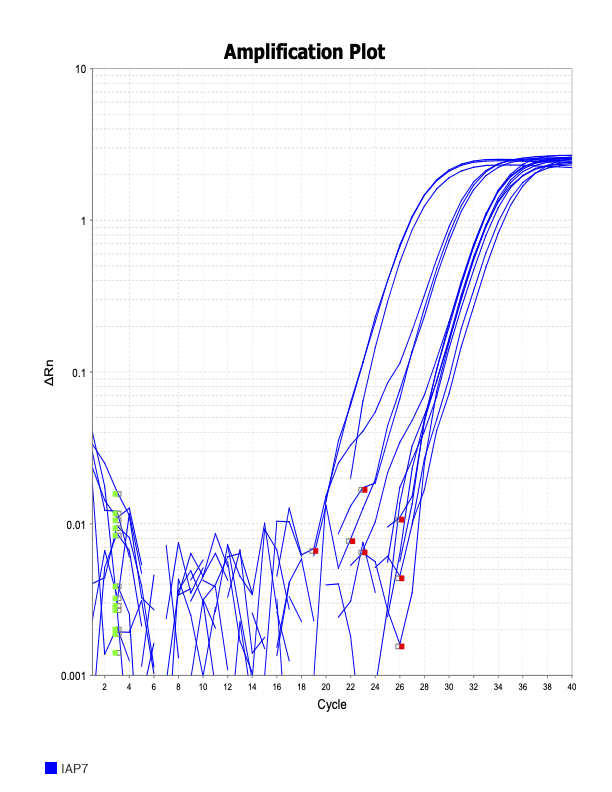
Trash
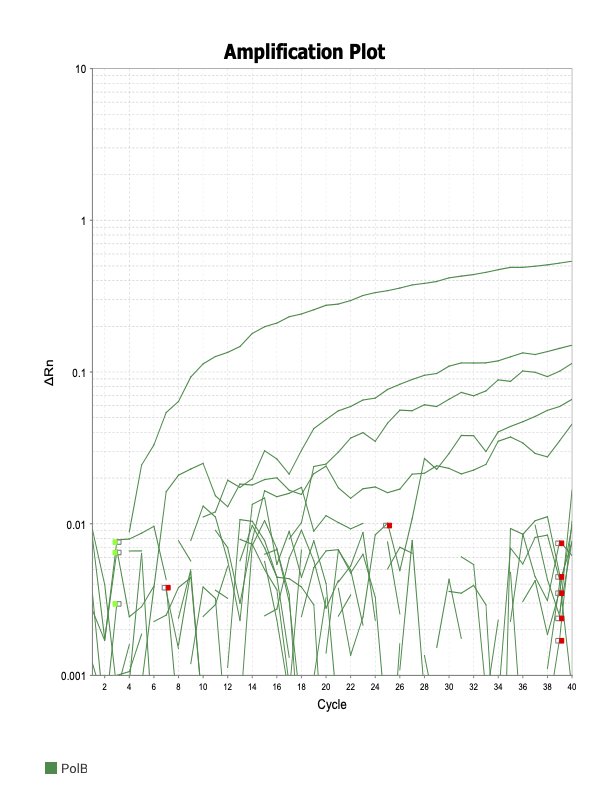
PolB
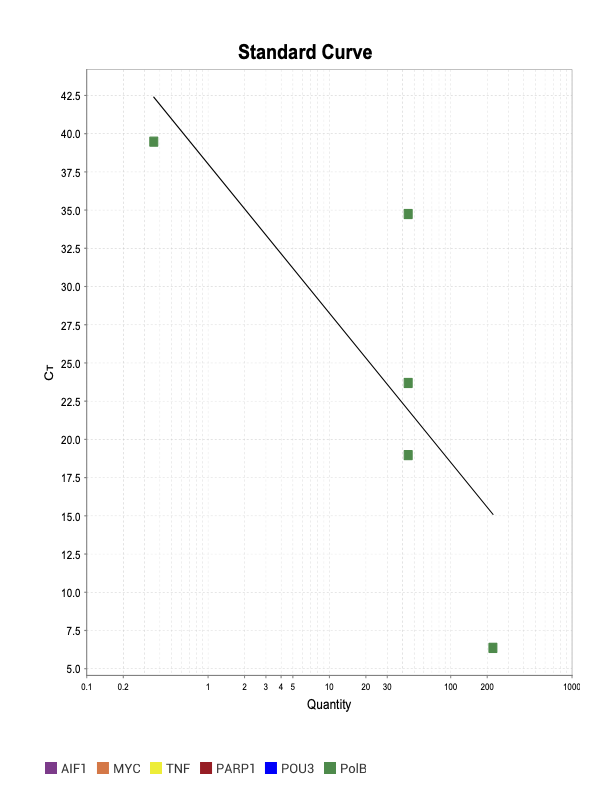
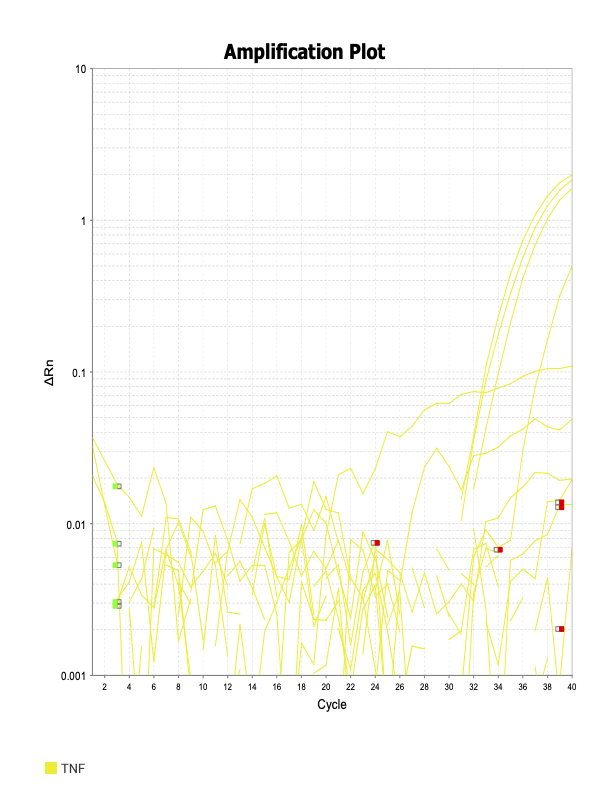
TNF

HSP70
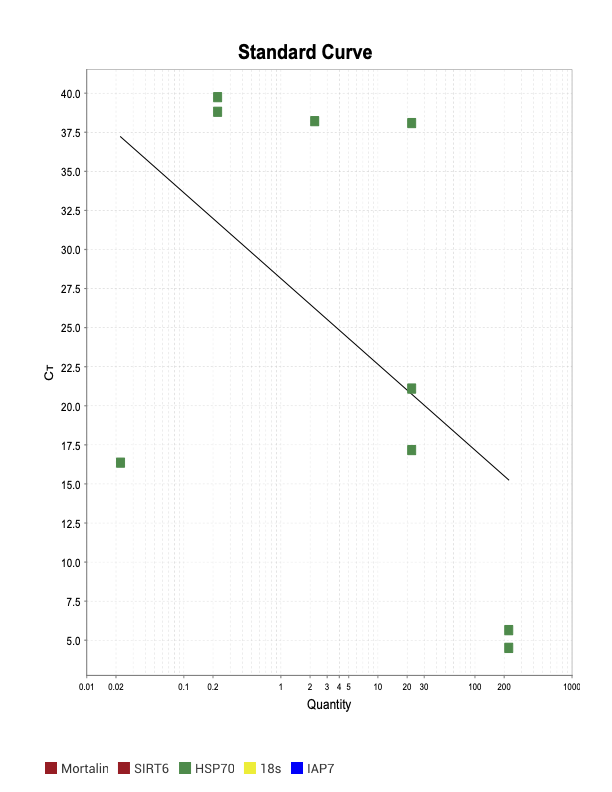

PARP1
Discussion
cDNA has low purity?
According to online sources DNA purity (260/280) should fall above 1.8. Currently the cDNA is at 1.7. RNA should fall above 2.0 (260/280). The RNA after gDNA elimination fell below that at an average of 1.71 (SD ± 0.12).
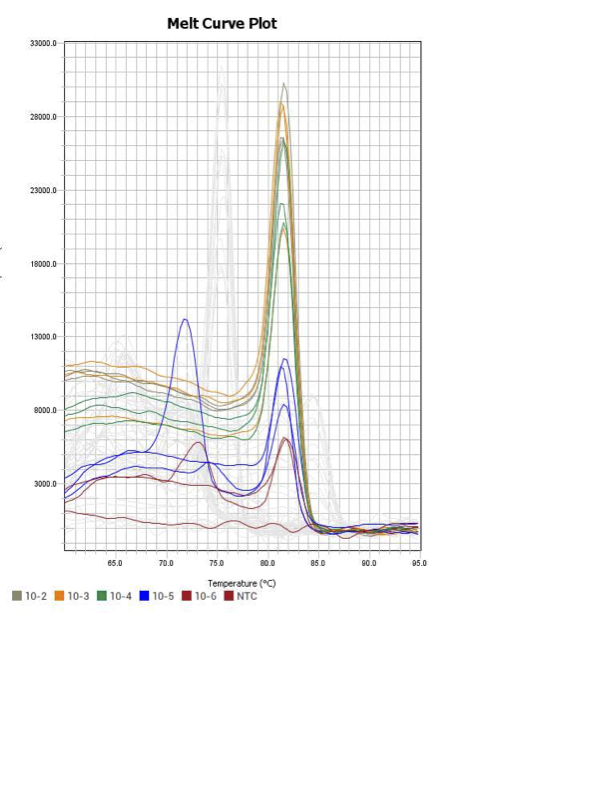
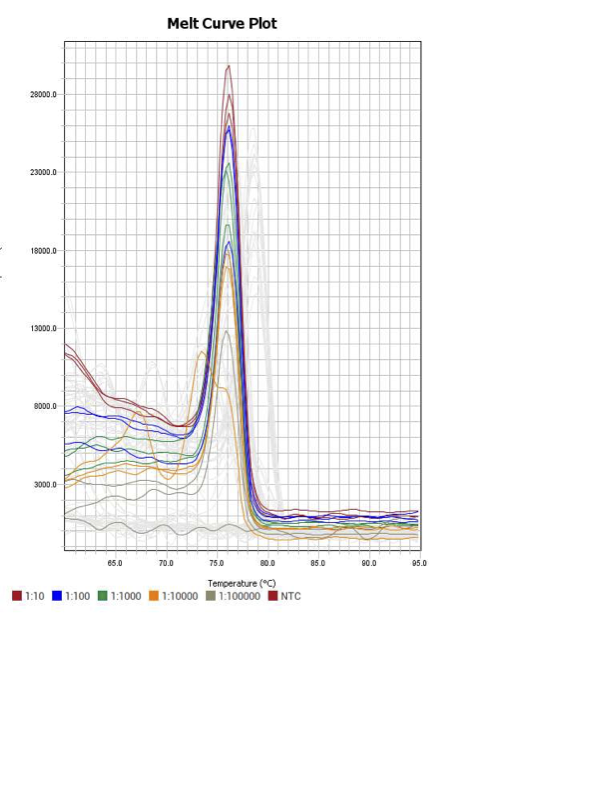
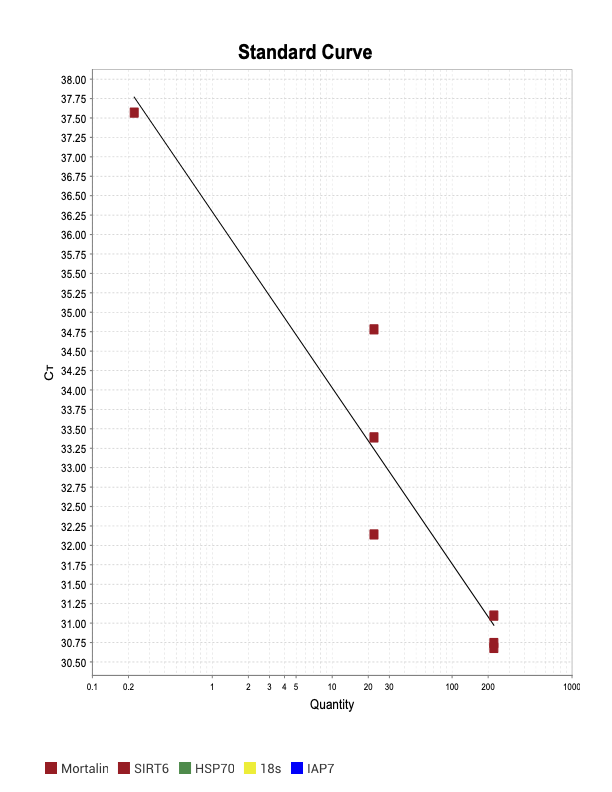
When running all the primer sets at a 1:5 dilution series, higher concentrations of cDNA resulted in a ‘horseshoe’ shape (indicative of failure to fluoresce) and most diluted sample (1:625) had lower Ct values than higher concentrations (1:125). Upon running a 1:10 dilution series, this issue is no longer as apparent. However, online sources mention that an amplification efficiency above 100% (which is what we see for nearly all the primers) or a really flat slope on the standard curve is indicative of polymerase inhibition.
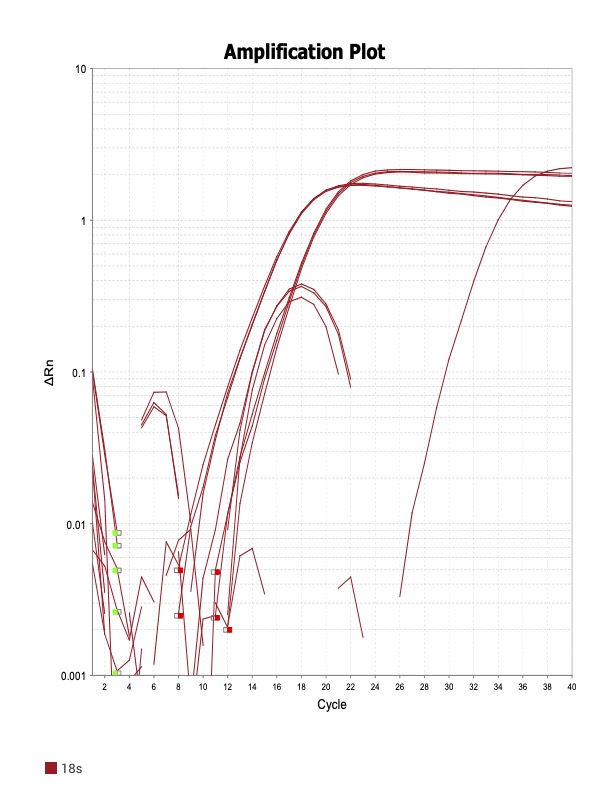
Common contaminants:
hemoglobin
polysaccharides
proteinase K
ethanol (during the RNA isolation)
However, the purity of my RNA prior to gDNA elimination was on average 1.89 (SD ± 0.11) so likely reagents fromt the gDNA elimination step were carried over into my samples.
Primers are not optimally designed?
Only workable primer sets will be those with a singular peak and appear to fail to have an acceptable efficiency curve due to high standard deviation across replicates.
The following primers currently in stock will be utilized moving forward:
Potentially Workable Primers of the Bunch
| Number | Gene | Forward Primer (5’-3’) | Reverse Primer (5’-3’) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BAX | CATTGACCTTGCGTGTTATTGG | AAGATGTCCTTGGTGGGTTG | in house |
| 7 | AIF1 | GGATTCTCTCACCGATGGAATAG | CCTGACTTGGAGCCTTTATGG | in house |
| 10 | SIRT6 | ATTAGTACCGCGTCTGGAATAC | GGATGGAATCGCTTCTTCAAATC | in house |
| 13 | Mortalin | TTCATGATACCGAAACCAAGATGGACG | AATTTCCTCCTTGATGGCATCCACC | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.023 |
| 14 | ACTb | GTAGGTAGTCTCGTGAATTC | CACGCCATCTTGCGTCTGGA | doi:10.1016/j.dci.2006.12.009 |
| 15 | 18s | GGCAGCCTCCGGGAAACCAAAGTC | CTGGTGGTGCCCTTCCGTCAATTC | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.023 |
Work arounds
Include Clean Up Step
Issue may lie completely with the low quality of the RNA at the moment. Using different primers potentially wouldn’t improve outcome since the puritiy falls bellow the acceptable threshold.
Alternative Primers
Further literature search regarding previous work conducted with B. schlosseri and qPCR resulted in finding the following paper:
Rosner A, Kravchenko O, Rinkevich B. IAP genes partake weighty roles in the astogeny and whole body regeneration in the colonial urochordate Botryllus schlosseri. Developmental Biology. 2019 Apr;448(2):320–41. doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015
This paper utilizes several primer sets targeting genes in relation to apoptosis. The following primer sets are pulled from this paper:
Proposed Primers
| Gene* or Accession** number | Gene name | Forward primer | Reverse primer | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g5785 | IAP6 | CTGGTATTGTAACGGCGGCCTGCAA | GGTGAACGAAATGCTGGCCTTTGGA | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g7904 | IAP8 | ATTTACCTCGGACGTTAGCGCAGGAC | CCCGGAACAAGAGAAGCATTGAACTC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g7149 | IAP9 | GGATGCGGGATATGCGGAGGATAG | AGCTTCCGCCGACTGATAGCATG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g27485 | IAP14 | GCGTGACCGTGTGAAATGCTGG | CCACTTTGCATGCTCGACCCAC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g44848 | IAP15 | ATGGAAGCCACCGACGAGATGAG | TCGATAACGTTCTGTTGGCAGCTCTTG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g56072 | IAP18 | TAAGCACATTCATGCGGTGGTCG | GCCCAAATAGAACAATCCGCAGTCTG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g29315 | IAP21 | CGTGAGCCTCTACTGCGCACTTCTC | GCTTGAGTAGAAGTTGGCGCAGAGC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| KU948200.1** | Bax | ATCTAGGCCAACCCGACCGAGAACC | CAACAGCTCCCTGGACCAAAGACG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| KU948202.1** | AIF1 | GGTGAGCAAGGGCATAGAAC | TGAACGACTCCGTGTTTGG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g8767 | caspase 2 | TGGTGAAGGTCCTGGCGAAGAAC | GCCTTTAACGACGCTGTTGACGG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g11647 | caspase7.1 | GCACAAATTCCGTGGTTGCTTCC | TTCTCTTGTCTCTGTGCGTCCCGTTTC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g3334 | caspase9 | GAAACCGATCTTACCGCCTACAACATG | ACGCATATATCAGATCGTCCTTGTTGC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g49756 | AKT1 | CTTGAAGACAATGATTACGGCAGGTCC | AAGCGTCCGCACATCATCTCGTAC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g1445 | PIK3CA | CTGATAAGGAAAGTCCACGGCAACGAC | CTGACCGGTTTGACGTGGAGTAATTG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g42386 | GSK3b2 | GTTTCCGCAAATCAAGGCTCATCC | TGCTACATAAACCGATGGCGTCCTG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g12744 | cdc25 | GAAATGTTCCCTGCCCACTGTGAC | CGATGCCGTGTTCTTTCTTCAGAGC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g41847 | myc | GCAGATCAGGGCCGCTCACAATGTC | TGTCGCGCAGCGTCAAGAAGGAAG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g61081 | sox2 | ACGCAGTTAATCATCATCCATCTCACC | AACCGGGATGTGGGCTACTTGC | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g68340 | hsp90α 3_1 | AAGATCATTTAGCCGTCAAGCACTTCTC | GGGCACGCTTTGGAACGAAGAG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
| g67511 | hsp90β 2_4 | AAGGCCCAGGCTCTTCGTGACTCTTC | GAGTGTTCGGGATTGATCTCCAAGTG | doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.10.015 |
*Gene number assigned by the Botrullus Genome Project (Voskoboynik et al., 2013).
**Accession number assigned by the NCBI GenBank.
Of the suite of IAPs reduced from the ones used in the referenced paper to capture those that were most interesting under oxidative stress at stage A and across blastogenic stages.
In our study we did not target a specific stage for oxidative stress (nickel) exposures so I believe it would be interesting to capture IAPs impacted by both factors.